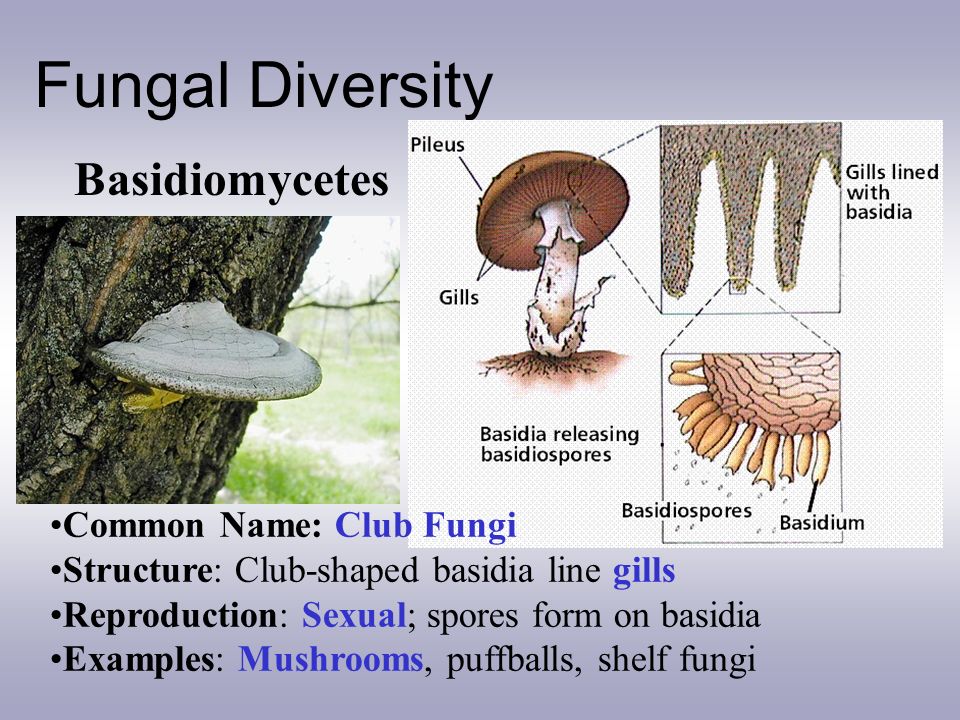
Ergosterol the functional equivalent of cholesterol found in cell membranes of fungi and some protists, as well as, the steroid precursor of vitamin D2; Club Fungi Fungi Quiz Diagrams Diagram Of Rhizopus Mycelium Club 123vielgeld De Template The Fungus Among Us Labelled Parts Of A Mushroom Diagram Of A Mushroom Illustration Biology Life Cycle Mushroom Diagram Stock Vector Hand Drawn Mushrooms Vector Illsutration Vector Mushroom Go Green Diagram Of Mushroom Diagram Data PreThe Basidiomycota (basidiomycetes) are fungi that have basidia (clubshaped structures) that produce basidiospores (spores produced through budding) within fruiting bodies called basidiocarps (Figure 8) They are important as decomposers and as food This group includes rusts, stinkhorns, puffballs, and mushrooms

Club Fungi Large Images Page 2
Club fungi diagram
Club fungi diagram-Georgette drew a diagram to compare chytrids and sac fungi Which description belongs in the area labeled Z?This single celled spores are born in a club shaped structure called basidium;




Diagram Cell Label Diagram Fungus Full Version Hd Quality Diagram Fungus Zodiagramm Prenotasanvito It
28 Diagram Of Fungi Basidiomycota Club Fungi Jelly Fungi Fungal Cell Diagram Top Electrical Wiring Diagram Cell Wall Plant Fungal Bacterial Structure And Functions Cell Wall Accumulation Of 35 S Labeled Cryparin A Min Pulse OfStart studying Club, Sac, or Zygote Fungi Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsJared drew a diagram to compare zygote and club fungi wich discription belongs in the area labled x 1Contain numerous flagella 2Are multicellular 3Produce spores 4Have
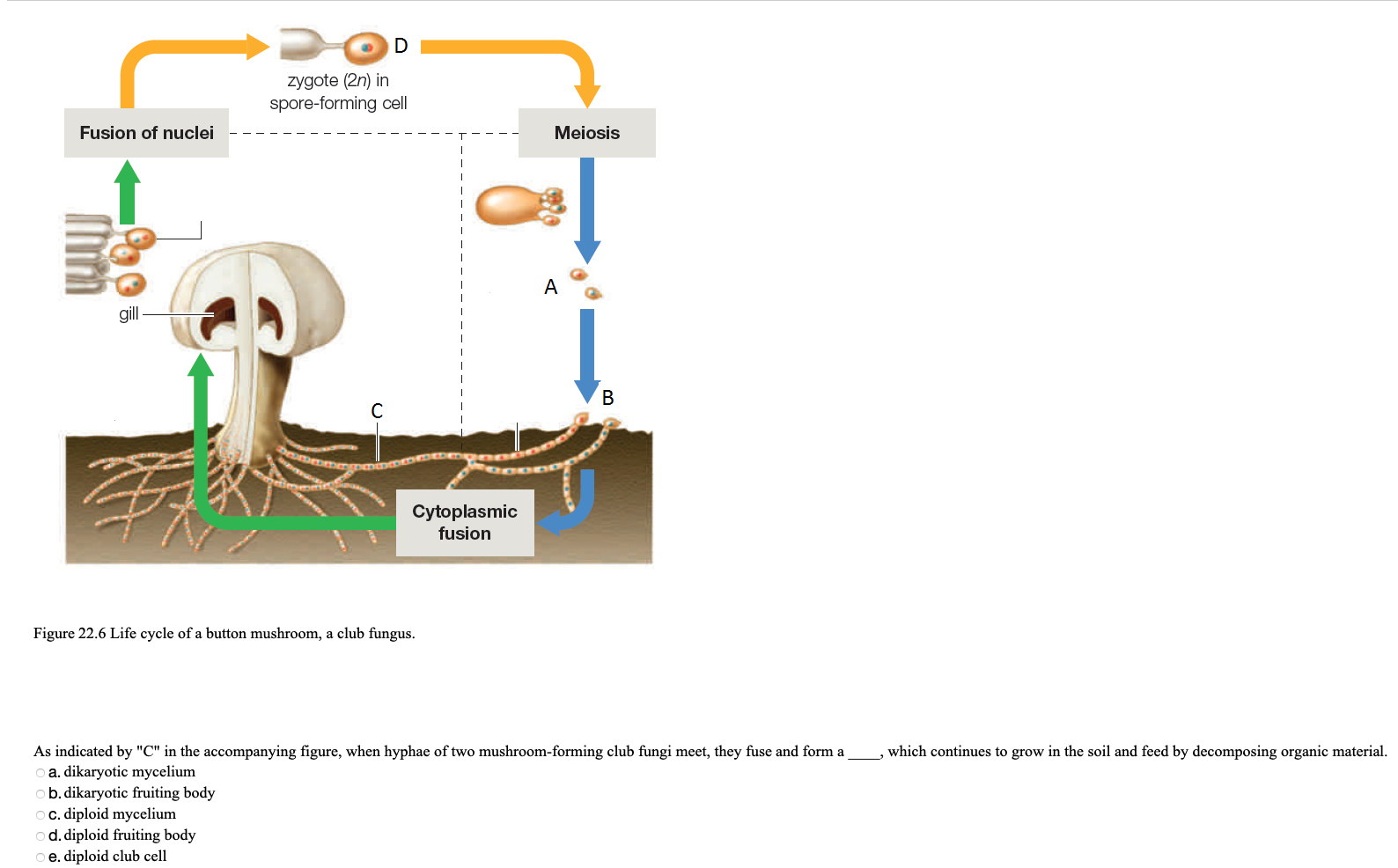
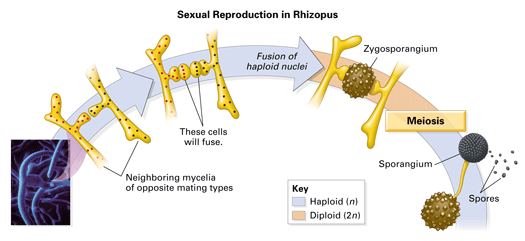
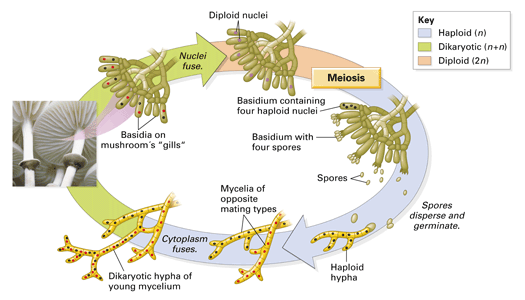
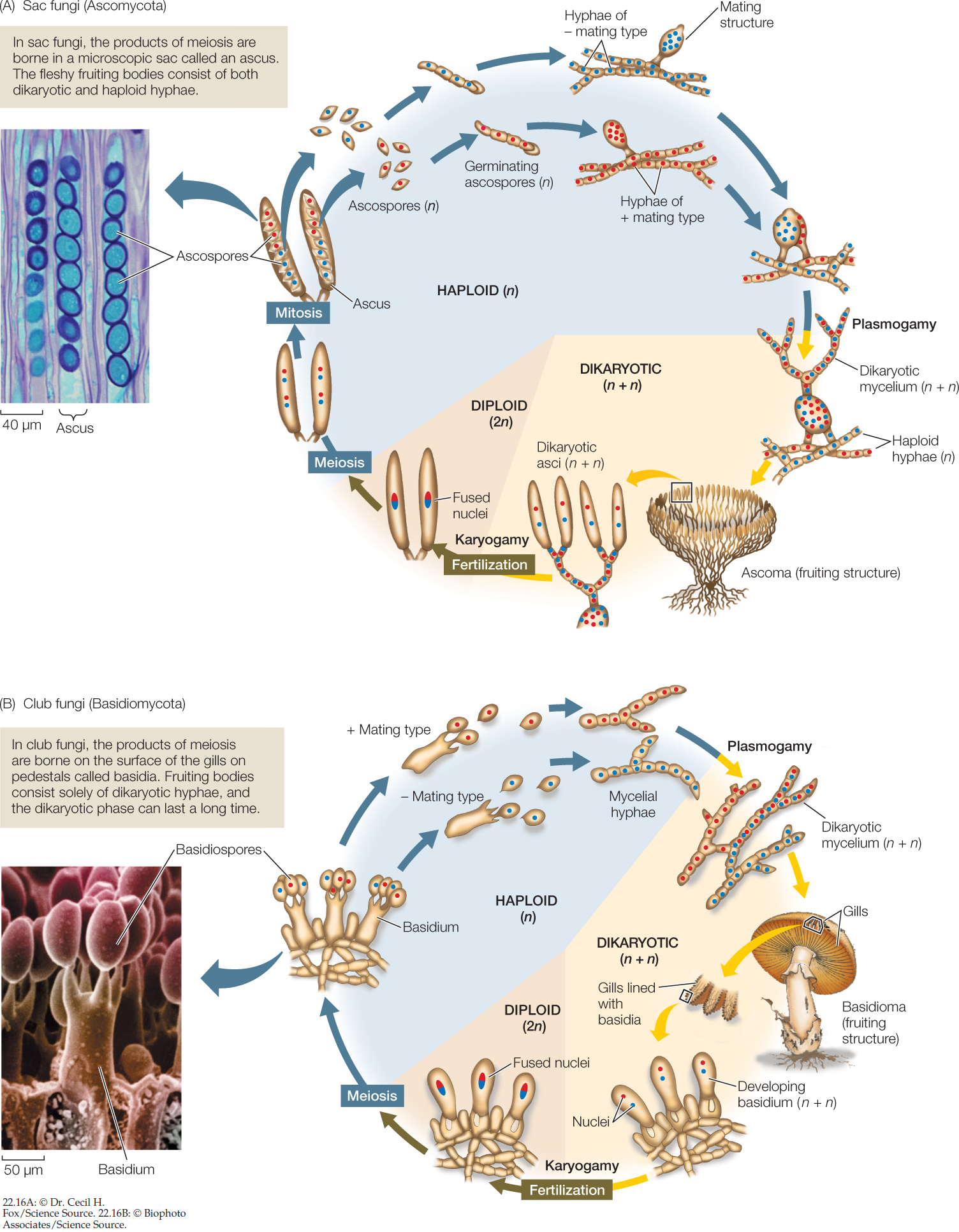
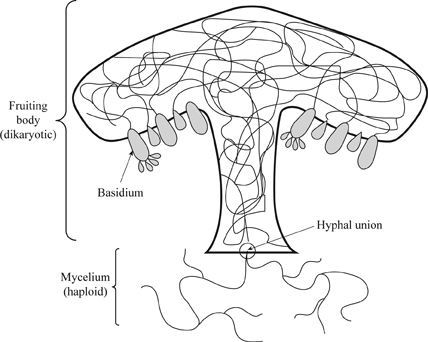
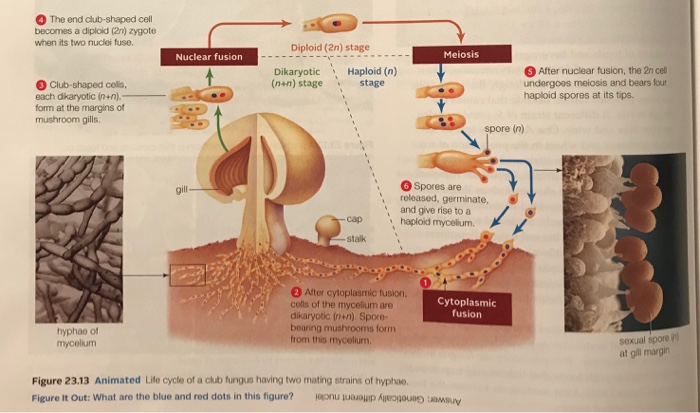
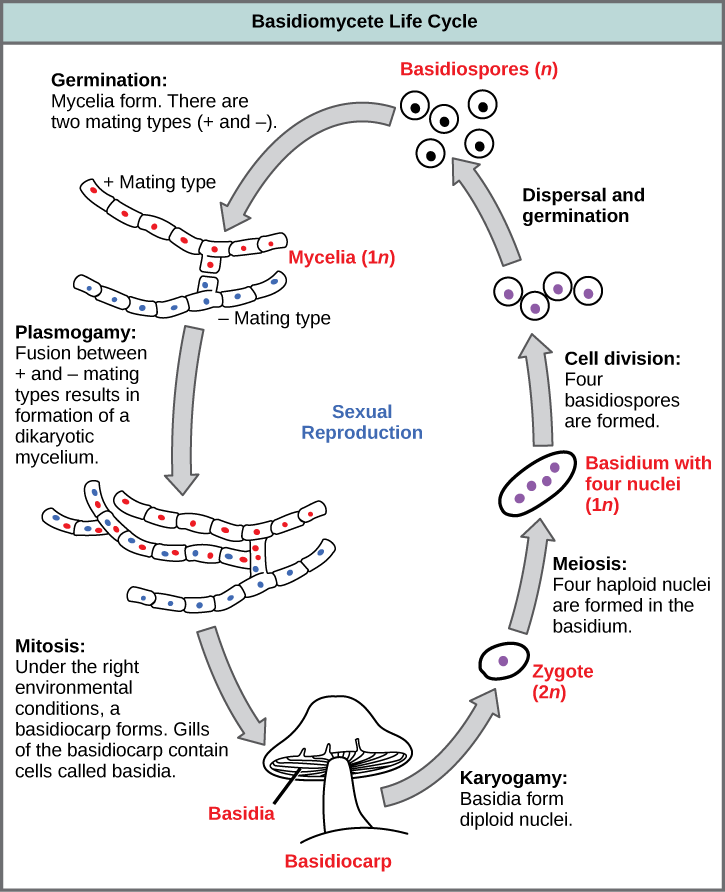
Fungi General characteristics Eukaryotes, whose cells contain membranebounded nuclei, mitochondria & other organelles Cell wall is composed of chitin, a polymer that consists of subunits of a nitrogencontaining sugar Chitin is highly resistant to enzymatic breakdown Structure of Chitin Fungi lack chlorophyll and are nonphotosynthetic These fungi follow some version of the life cycle in Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) below Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) Generalized life cycle of the mushroomforming basidiomycetes (Agaricomycotina) On the right side of the diagram, haploid basidiospores of two different mating types produced (dark blue and red)These basidiospore aerves as main air dispersal unit for the fungi iii Zygospore Zygospores are thick walled spores formed when two sexually compatible hyphae or gametangia of certain fungi fuse together
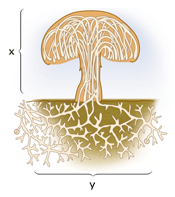
Basidium a microscopic, clubshaped sporebearing structure produced by certain fungi Basidiocarp the sporocarp of a basidiomycete, the multicellular structure on which the sporeproducing hymenium is borne Mycelium the vegetative part of a fungus, consisting of a network of fine white filaments (hyphae)X 2 x amp y 3, mycelium septate aseptate zygote fungi sac fungi club fungi zygosporangium draw and label a diagram that illustrates the structure of a typical fruiting, hyphae fungi cell diagram electric stove wiring diagram wiring diagram for car stereo f150 cantilever beam shear and moment diagramThe diagram below shows the generalized life cycle of fungi Phylum Basidiomycota (Club Fungi) Some examples of basidiomycetes are mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungi, birds nest fungi, and stinkhorns This group includes some serious plant diseases such as rusts and smuts



D Zygote 2n In Spore Forming Cell Fusion Of Nuclei Chegg Com



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2
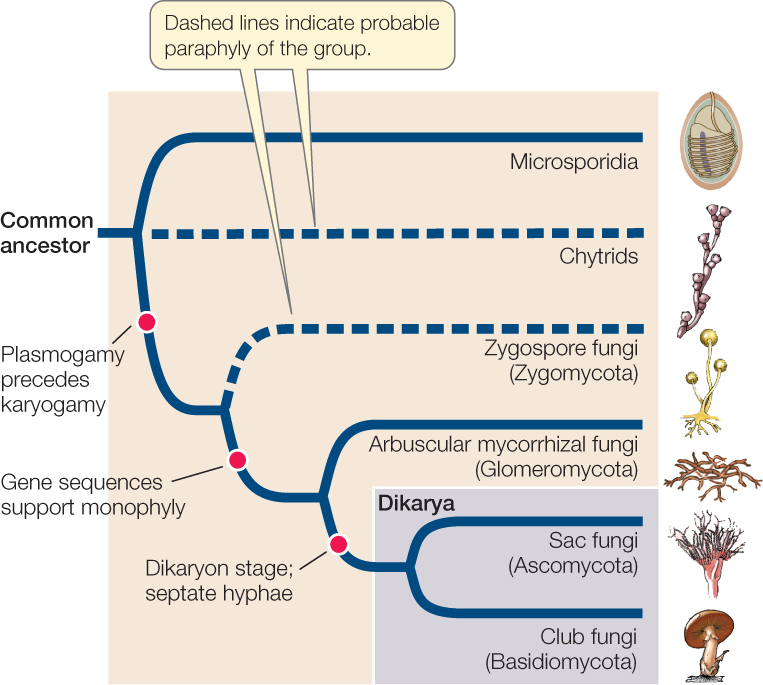
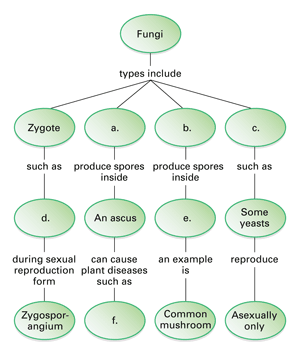
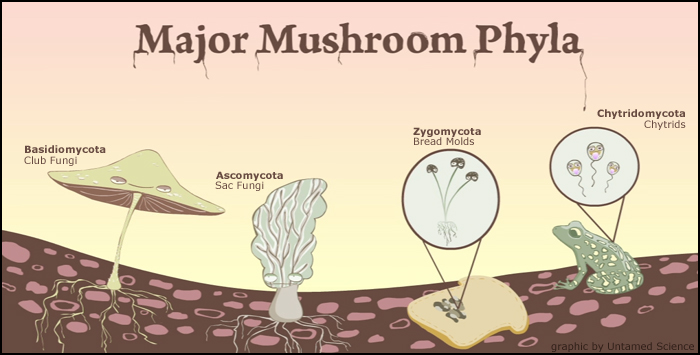
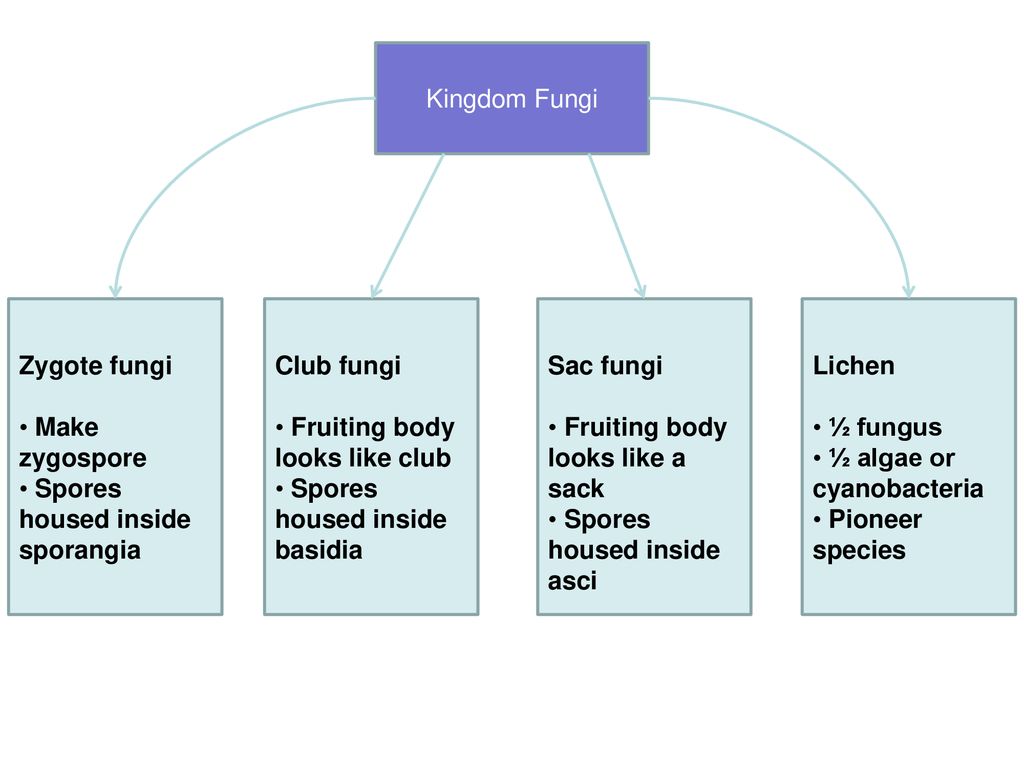
The five true phyla of fungi are the Chytridiomycota (Chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), the Basidiomycota (club fungi) and the recently described Phylum Glomeromycota An older classification scheme grouped fungi that strictly use asexual reproduction into Deuteromycota, a group that is no longer in useTypes of fungi Fungi are subdivided on the basis of their life cycles, the presence or structure of their fruiting body and the arrangement of and type of spores (reproductive or distributional cells) they produce The three major groups of fungi are Multicellular filamentous moulds Macroscopic filamentous fungi that form large fruiting bodies3 Reproduce by mitosis What is the scientific name for the "club fungi"?



Life Cycles Of Fungi Biolympiads




Beefsteak Fungus Polyporales Species Britannica
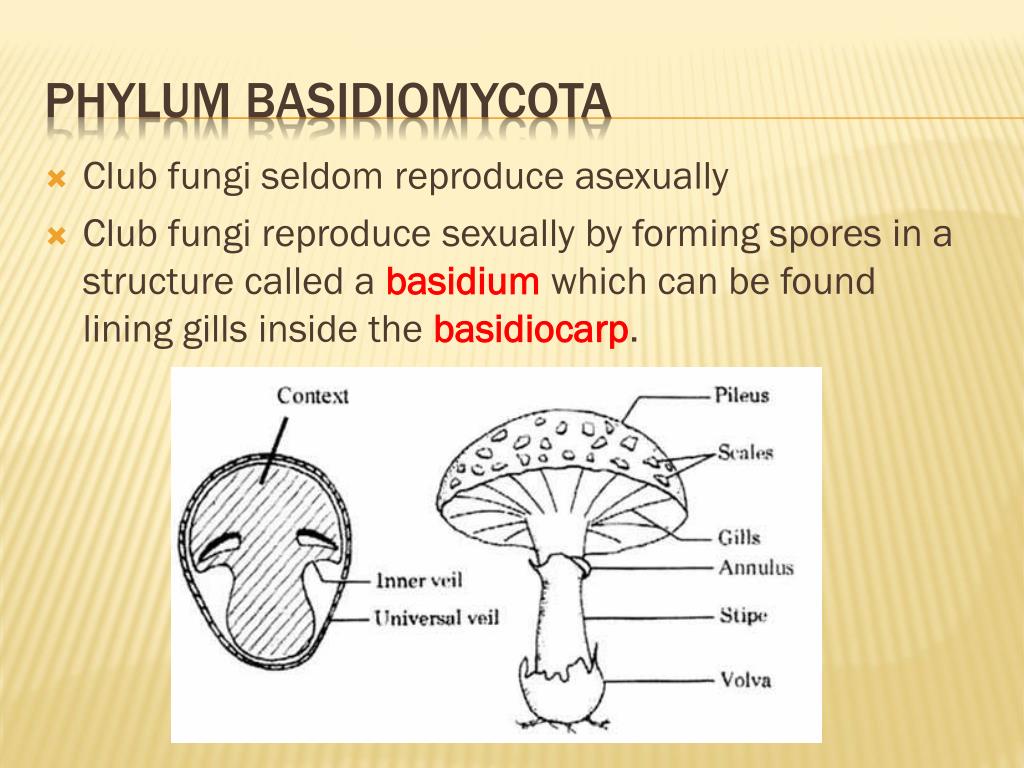
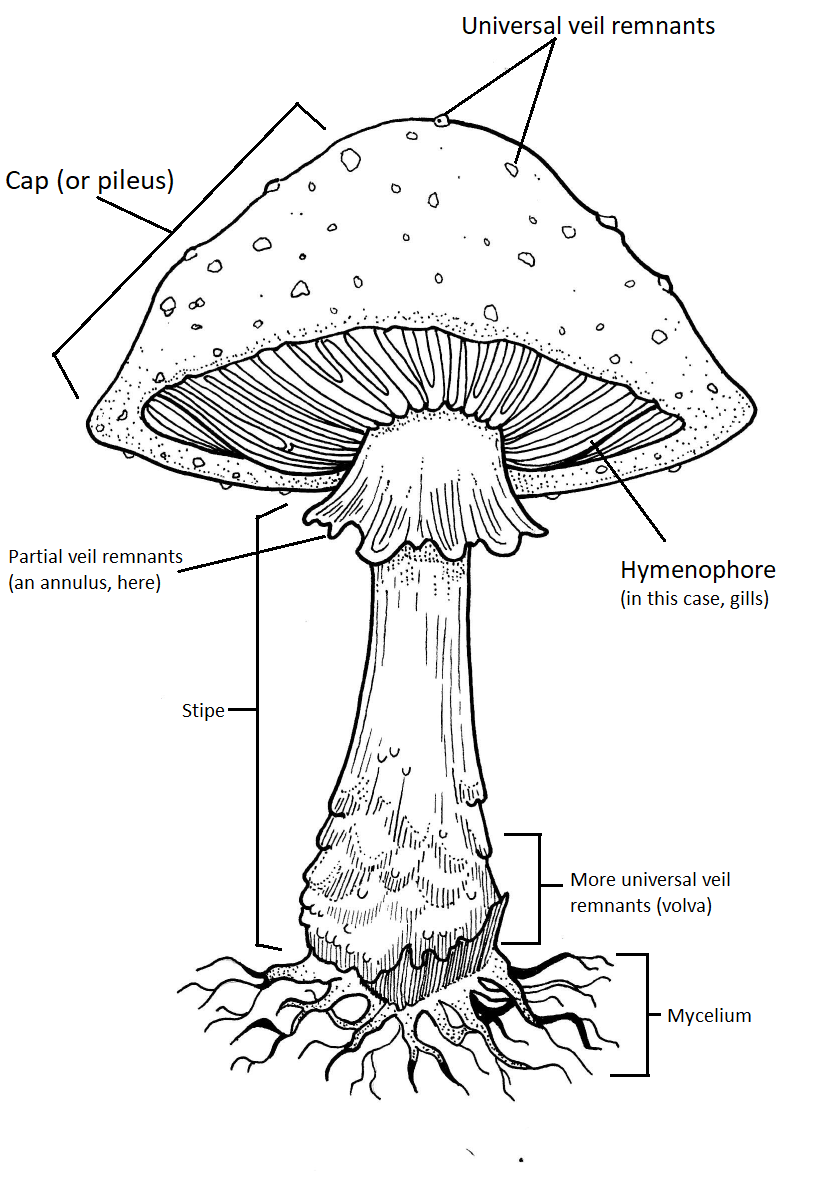
The Fungi Kingdom 2 Basidiomycota (Club fungi ) have a clubshaped part which produces the spores 3 Ascomycota (Sac Fungi) produce spores in saclike structures EX yeasts, cup fungi, powdery mildews, & lichens Lichens 4 Types of Fungi a fungus and an organism with chlorophyll (cyanobacteria or algae) that live together The cap of the mushroom is the topmost part This is a thumbnail of the label the mushroom anatomy diagram Label the cap stipe and gills Cap pileus the top part of the mushroom Rhizopus and mucor are the common saprotrophic fungi that attack a variety of food stuffs Mucor pusillus causes infection of internal organs in human beingsEcology Bracket fungi often grow in semicircular shapes, looking like trees or wood They can be parasitic, saprotrophic, or bothOne of the more common genera, Ganoderma, can grow large thick shelves that may contribute to the death of the tree, and then feed off the wood for years afterTheir hardiness means they are very resilient and can live for quite a long time, with many




Club Fungi Reproductive Structures Are Shown In The Image Below What Benefits Are There In Having Brainly Com




Diagram Blank Fungi Diagram Full Version Hd Quality Fungi Diagram Stereodiagram Newsymposium It
最新 club fungi labeled Club fungi labeled Posted by Leave a comment on label the life cycle of fungi Leave a comment on label the life cycle of fungi6 Are all mushrooms edible?Basidiocarp, also called basidioma, in fungi, a large sporophore, or fruiting body, in which sexually produced spores are formed on the surface of clubshapedStructure that resembles a club 4 The reproductive structure is called a basidium 5 Fungi in this phylum do not appear to have a sexual phase in their life cycles Reviewing Key Skills Interpreting Graphics Use the diagram to answer the following questions on the life cycle of a zygomycete Sporangium Spores (N) Sporangiophore A Zygospore (N)The traditional divisions of Fungi are the Chytridiomycota (chytrids), the Zygomycota (conjugated fungi), the Ascomycota (sac fungi), and the Basidiomycota (club fungi) An older classification scheme grouped fungi that strictly use asexual reproduction into Deuteromycota, a




30 Diagram Of Mushroom With Label Labels Design Ideas




Which Type Of Fungus Is Shown In The Diagram Brainly Com
Basidiomycetes (myc=fungi) What type of reproductive structure is produced by the club fungi?The vast majority of fungi are multicellular and terrestrial, although about 500 species are marine The kingdom is classified into three phyla or divisions the Zygomycota (zygosporeproducing fungi), Ascomycota (sac fungi), and Basidiomycota (club fungi) Fungi have pronounced effects on human societies, both positive and negativeThe pinheads (baby mushrooms) are easy to spot when you know what they look like




The Fungi Kingdom Mycology The Study Of Fungi Fungi Singular Ppt Video Online Download



Fungi
The hyphal knot is the first point at which the pinhead and body of the mushroom begin to sprout but not yet take form The transition from hyphal knots to the baby mushrooms, also called pinheads, is a process visible to the naked eye From Pinning to The Mushroom!The Club Fungi Eric Swann and David S Hibbett This tree diagram shows the relationships between several groups of organisms The root of the current tree connects the organisms featured in this tree to their containing group and the rest of the Tree of Life The basal branching point in the tree represents the ancestor of the other groupsADVERTISEMENTS In this article we will discuss about the life cycle of basidiomycetes with the help of suitable diagrams Mycelium of Basidiomycetes The well developed, filamentous mycelium consists of a mass of branched, septate hyphae generally spreading in a fanshaped manner The cell wall is chitinous in nature Within the cell wall is the plasma




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual




Vocabulary Chitin Ppt Video Online Download
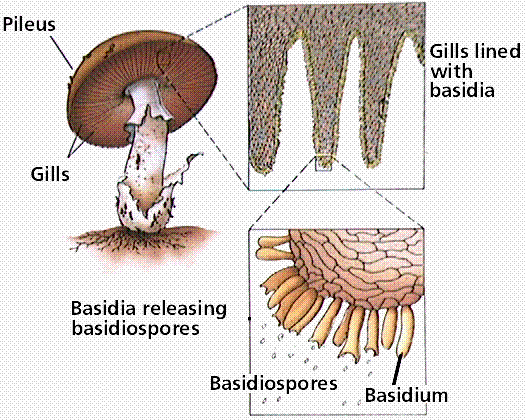
Members of the Basidiomycota, commonly known as club fungi, produce spores called basidiospores on clublike stalks called basidia Most common mushrooms belong to this group, as well as rust and smut fungi, which are major pathogens of grainsHypha a long, branching, filamentousBasidomycete Club fungi •Cap • Gills spores Examples Puffballs Shelf fungus Stinkhorns Fairy rings Imperfect fungi • We do not know how their sexual reproduction takes place • Penicillium spp Lichens • Symbiotic relationship with algae or cyanobacteria and a




Jared Drew A Diagram To Compare Zygote And Club Fungi Which Description Belongs In The Area Labeled Brainly Com




Basidiomycota
Sac Chytrid O Have reproductive cells with flagella O Contain cell walls O Release chemicals to break down food O Lack hyphae 3 Answers (2) Rishi House 2The fourth, and final, division in the kingdom Fungi that we will cover is the phylum Basidiomycota This is the phylum that you are probably most familiar with because it contains fungi which are generally referred to as gilled fungi or gilled mushrooms However, with over 25,000 classified species, it also houses diverse members such as puffballs, shelf fungi, and rusts (which are4 At one point scientists classified fungi as plants Complete the diagram below by bulleting the similarities and differences of plants and fungi Plant Evolution/Origin of Plants 5 Land plants evolved from green algae 6 List the similarities between land plants and their ancestor a




Basidiomycetes Biological Classification Vinay Biology Youtube




Fungi Flashcards Quizlet
2 When mushrooms make a large circle in your yard, what is it called?A club fungi C imperfect fungi B common molds D sac fungi In your textbook, read about club fungi and the life cycle of a mushroom Label the diagram of the mushroom and parts of its life cycle Use these choices basidium caps spores Unit 5 CHAPTER Fungi 23 24 25In ascomycota (sac fungi), the ascospores were enclosed in an ascus In basidiomycota, the basidiospores are not enclosed Compare the diagrams of a basidium with basidiospores above with that of an ascus with ascospores seen earlier Basidiospores germinate to produce monokaryotic (haploid, one nucleus per cell) hyphae



Vocabulary Chitin Ppt Video Online Download




Kingdom Fungi Cont Flashcards Quizlet
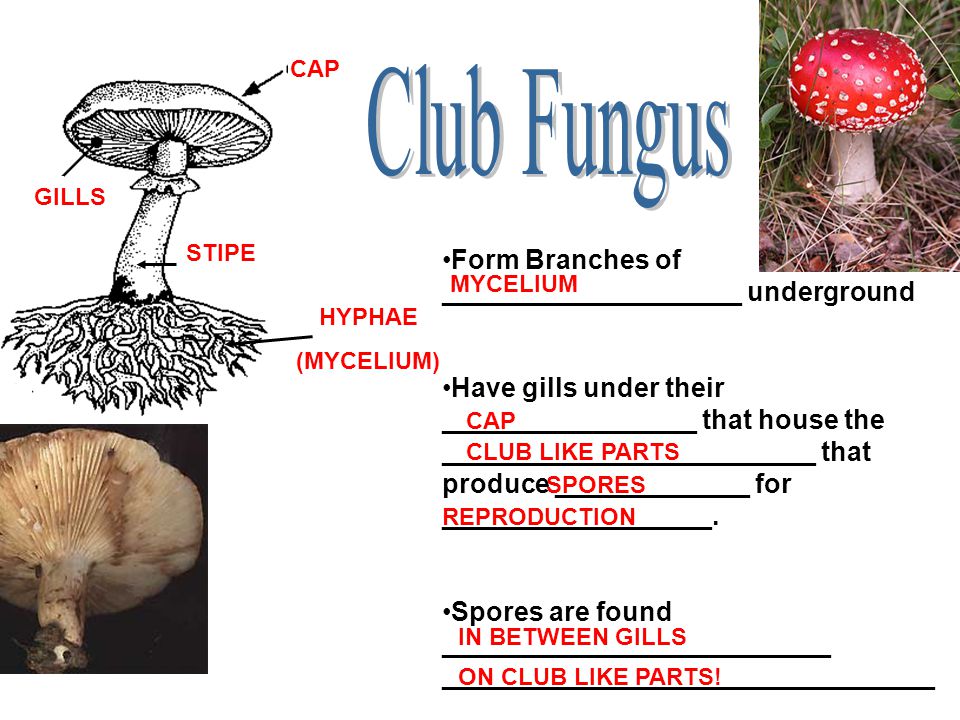
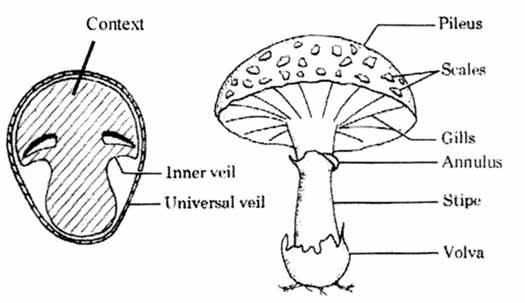
The 5 Parts of a Mushroom and its Characteristics The Parts of a fungus Can be divided into volva, stipe, hymenium, pileo and internal parts A fungus or mushroom is a large eukaryotic organism with a fruit structure that can grow above or below the earth, having a different classification for each case These macrofungi can have a height andCHAPTER 14 Fungi structure and reproduction Introduction Section "A" The fungi are a group of eukaryotic, nonvascular organism Which are of diverse forms, sizes, physiology and reproduces both by sexual (meiotic) and asexual (mitotic) sporesExamples of fungi Mushrooms, yeasts, molds, Penicilliumthe first of the wonder drugs, penicillin, was isolated from this fungus andThe common mushroom Use a labeled diagram to describe the cap and gills of a club




Fungi Diagram Quizlet
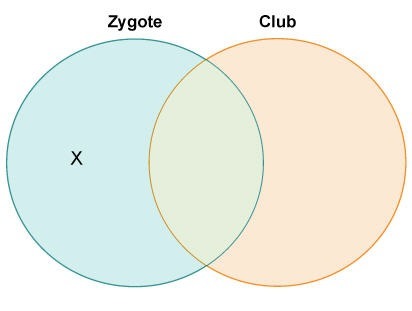



Plz Answer Correctly And Quickly Jared Drew A Diagram To Compare Zygote And Club Fungi Which Description Belongs To The Area Labeled X Contain Numerous Flagellaare Multicellularproduce Sporeshave Loo Studydaddy Com
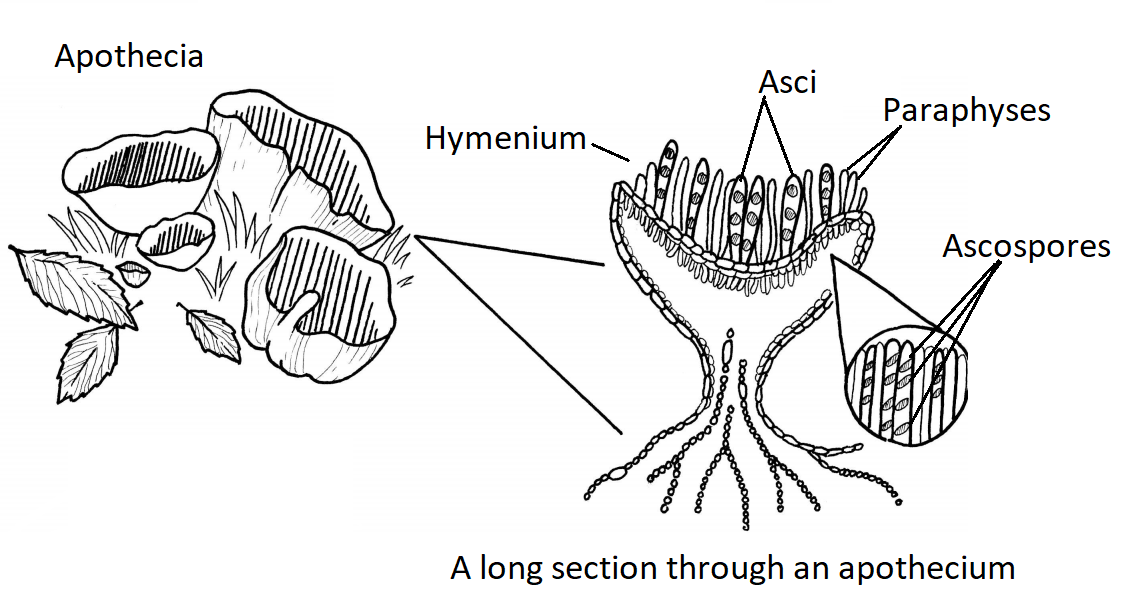
Diagram of an apothecium Members of the Basidiomycota, commonly known as the club fungi or basidiomycetes, produce meiospores called basidiospores on clublike stalks called basidia Most common mushrooms belong to this group, as well as rust and smut fungi, Basidiomycetes – The Club Fungi 1 Basidiomycetes (Gk basidium small base, mykes fungus) are the most advanced and most commonly seen fungi as their fructifications are often large and conspicuous, eg, mushrooms (gill fungi), toadstools, puff balls, bracket fungi, etc 2 The class contains about 25,000 species 3 Key Terms glucan any polysaccharide that is a polymer of glucose;




Classification Of Fungi Into 5 Phyla Flow Chart With Examples




Chapter Fungi Mushrooms C Frans Lemmens Corbis Copyright C Mcgraw Hill Education All Rights Reserved No Reproduction Or Distribution Without The Prior Ppt Download
Phylum – Club Fungi Club fungi are the typical types of fungi that we think of as a mushroom The fruiting bodies of the club fungi vary widely and are grouped by general characteristics such as the area or structure on which their spores are formed For instance gill fungi are club fungi that reproduce on structures called gillsThe fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their clubshaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hyphaThe basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves,Club Fungi are the most common of the Fungi and are umbrella like in shape (Use your book) What is the club like structure of the mushroom called?




Biology For Kids Fungi




Basidiocarp Wikipedia
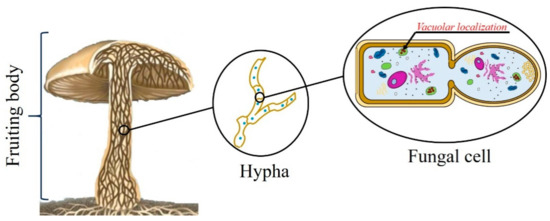
Mycelium the vegetative part of any fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, threadlike hyphae, often underground;The diagram shows this in stylized form and the photo shows a closeup view of a species of Clavicorona where you can see some very young branches developing around the rim of one of these disklike areas A number of puffballs (and their close relatives) are simply bags of spores, but that's not the case for all of these fungiApril 11th, 19 Diagram Of Aseptate Mycelium pdf Free Download Here WF01 Welcome to the World of Fungi British Mycological Society mycelium septate aseptate zygote fungi sac fungi club fungi zygosporangium gametangium mycelium remember aseptate coenocytic diagram Choose 2 bacterial strains and 1 fungal strain from the list below 2




Club Fungi Large Images Page 2



Fungi Antibiotics Yeasts Penicillium
Some basidia develop grooves under the cap of the mushroom, what are these called and what do some hold? Kingdom Fungi are classified based on different modes The different classification of fungi is as follows Based on Mode of nutrition On the basis of nutrition, kingdom fungi can be classified into 3 groups Saprophytic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by feeding on dead organic substances Examples Rhizopus, Penicillium and AspergillusFungi The division of fungi known as the club fungi, Basidiomycota, includes some of the most familiar fungi Mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi are all members of this group, as are the plant rusts and smuts This group, which contains approximately 15,000 known species, is distinguished by the presence of a club shaped reproductive organ




16 3 Macrofungi Biology Libretexts




Semoneapbiofinalexamreview N Fungi 31 Fungi Kingdom Fungi Teaching Biology
Diagram A Diagram B



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes




Reading Fungi Biology Ii Laboratory Manual




The Many Kinds Of Fungi



4 5 Macrofungi Biology Libretexts




Classifications Of Fungi Openstax Biology 2e




Exam Preparation Biology Study Material And Notes



1



Hillis2e Ch22



Http Www Hamilton Local K12 Oh Us Downloads 2 21 Fungi Kingdom Pdf




Tips For Identifying And Photographing Mushrooms The Canadian Nature Photographer




Kingdom Fungi 1 Introduction To Fungi Mushrooms Toadstools




Gill Fungi




Tiny Club Fungi Multiclavula Mucida Rock Creek Park Wash Flickr



Chapter 18 Concept 18 2



Chapter 18 Chapter Review




The Average Normalized Spectrum Of The Stalks Of The Three Types Of Download Scientific Diagram



Chapter 11 Protists And Fungi 7th Grade Science Kile Mingo



Bil 160 Lecture 18



6 L 5a 2 How Fungi Respond To External Stimuli South Carolina 6th Grade Science




Phylogenetic Relations Of Fungal Phyla Adapted From Bear Et Al 16 Download Scientific Diagram



Fungia Archives Untamed Science




Fungus Wikipedia




5 Types Of Club Fungi By Kaykay Jadyn



Life Cycles Of Fungi Biolympiads




Page 2 Club Fungi High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy



Toxins Free Full Text Ageritin From Pioppino Mushroom The Prototype Of Ribotoxin Like Proteins A Novel Family Of Specific Ribonucleases In Edible Mushrooms Html



Fungi




Hillis2e Ch22



Hillis2e Ch22



Glossary




Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap



Bil 160 Lecture 18



Fungi




Diagram Well Labelled Diagram Of A Mushroom Full Version Hd Quality A Mushroom Ezdiagram Prenotasanvito It



Teaching The Fungal Tree Of Life Home




Clavarioid Fungi Wikipedia




The Many Kinds Of Fungi



Basidiomycota




Fungi Basics Heterotrophs Cannot Perform Photosynthesis Release Enzymes To Absorb Nutrients Cell Composition Similar To Animals Reproduction Sexual Ppt Download




Ppt Club Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Chapter 18 Chapter Review




Club Fungi Kingdom Fungi Phylum Basidiomycota Fungi Kingdom Fungi Stuffed Mushrooms




Kingdom Fungi Diagram Quizlet




Club Fungi Diagram Quizlet




4 Basidiomycetes Club Fungi



Definition Of The Major Groups Of Fungi Chegg Com



Characteristics Of Fungi Ppt Video Online Download




Club Fungi Dykaryotic Life Cylce Diagram Quizlet



Fungi Ascomycota Sparknotes



Kingdom Fungi Ppt Download




Heterotrophs Fungi Basics No Photosynthesis Release Enzymes To



Fungi




Diagram Cell Label Diagram Fungus Full Version Hd Quality Diagram Fungus Zodiagramm Prenotasanvito It



Fungi Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Sparknotes



About Club Fungi



Please Help Me These Question In Each Diagram Please Chegg Com




Pop Up Post Fungi I D Walk In West Olympia Native Plant Salvage Foundation



Club Fungi



Phylum Basidiomycota The Basidiomycetes Club Fungi




245 Club Fungi Photos Free Royalty Free Stock Photos From Dreamstime



1



1




Chapter 21 Kingdom Fungi Notes Mysterious Molds Mildews



Amycochran Weebly Com Uploads 5 7 8 8 Fungi Characteristics Worksheet Pdf



Ppt Kingdom Fungi Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Learn About Club Fungi Chegg Com




Please Answer Asap The Diagram Shows The Inside Structure Of A Fungus Which Best Describes The Brainly Com




Club Fungi Flashcards Quizlet




Fungi Diagram Quizlet




Amy B S Bio Blog Fungi




Fungi And Lichens



3 6 2 Types Of Basidiocarps Biology Libretexts




Mushroom Morphology Types Of Identifying Characteristics



Basidiomycota



Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii



Basidiomycota


